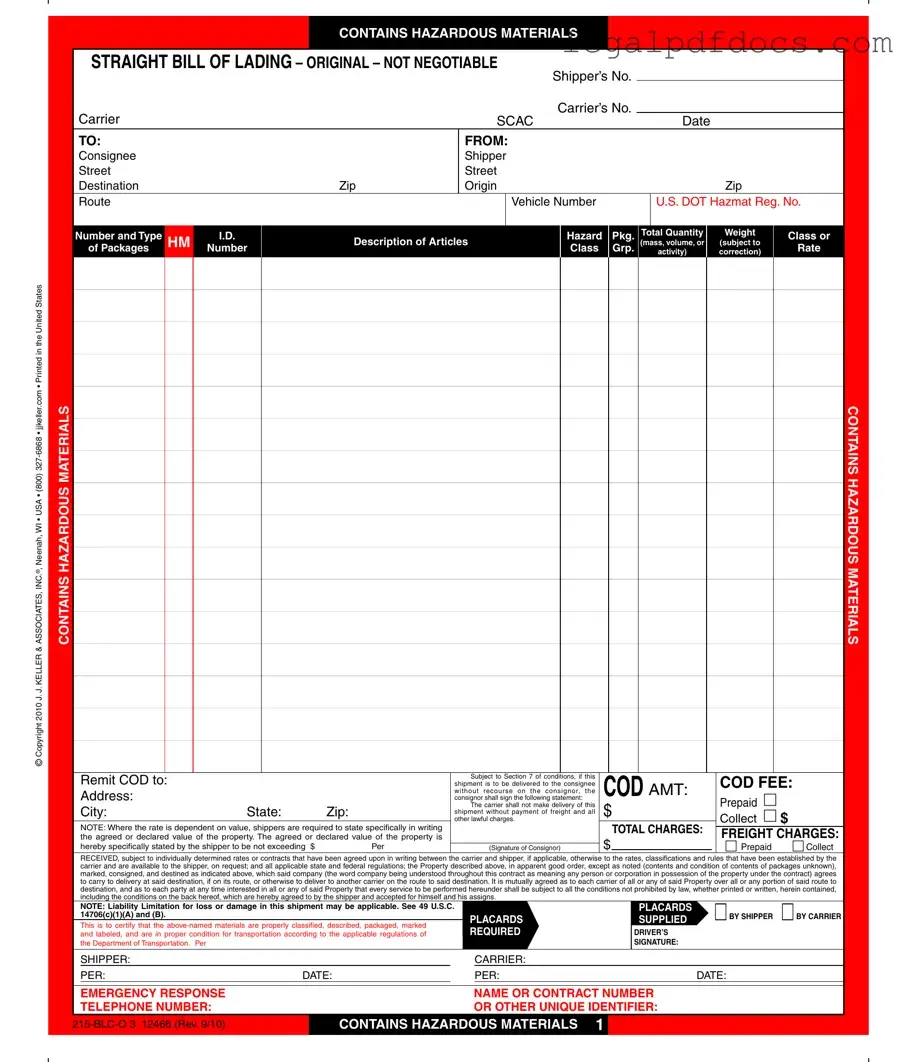
Fill Out a Valid Hazard Bill Of Ladden Template
The Hazard Bill of Lading form is a critical document used in the transportation of hazardous materials. It serves as a contract between the shipper and the carrier, detailing essential information such as the shipper and consignee's addresses, the nature of the hazardous materials being transported, and specific handling instructions. Key elements include the description of the articles, total quantity, weight, and applicable hazard classifications. This form outlines payment responsibilities, including freight charges and any additional costs associated with the shipment. It also emphasizes the importance of proper packaging and labeling, ensuring compliance with federal regulations. The form contains stipulations regarding liability limitations for loss or damage, along with procedures for filing claims. In cases where hazardous materials are involved, the form requires the shipper to certify that the materials are correctly classified and packaged. Understanding the nuances of this form is vital for anyone involved in the shipping of hazardous goods, as it impacts both legal and safety considerations during transport.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Hazard Bill of Lading form, it's essential to follow specific guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here are four things you should and shouldn't do:
- Do provide clear and accurate descriptions of the hazardous materials being shipped.
- Do ensure all required signatures are obtained before submitting the form.
- Do double-check the weight and quantity of the materials to avoid discrepancies.
- Do keep a copy of the completed form for your records.
- Don't omit any required information, as this could lead to delays or legal issues.
- Don't use vague language when describing the materials; specificity is crucial.
- Don't forget to check for any updates to regulations that may affect your shipment.
- Don't assume that previous forms are sufficient; each shipment may have unique requirements.
How to Use Hazard Bill Of Ladden
Filling out the Hazard Bill of Lading form requires careful attention to detail. Each section must be completed accurately to ensure compliance with regulations regarding hazardous materials. After completing the form, it will need to be signed and submitted to the appropriate carrier for processing.
- Shipper's Information: Enter the shipper's name, address, and contact information in the designated fields.
- Consignee Information: Fill in the consignee's name and address, including the street, city, state, and zip code.
- Carrier Information: Provide the name of the carrier and their SCAC code in the respective boxes.
- Date: Write the date of shipment in the specified format.
- Hazmat Registration: Include the U.S. DOT Hazmat Registration Number.
- Description of Articles: Clearly describe the hazardous materials being shipped, including the number and type of packages.
- Weight and Class: Indicate the total weight and the class of hazardous materials, as applicable.
- COD Information: If applicable, fill in the COD amount and COD fee, and check the appropriate boxes for prepaid or collect.
- Total Charges: Calculate and enter the total charges, including freight charges.
- Signature of Consignor: The consignor must sign and date the form in the designated area.
- Emergency Response Information: Provide the name or contract number and telephone number for emergency response.
More PDF Templates
Cadet Command Forms - Students are encouraged to recognize the importance of all requisite credit hours.
Pdf Puppy Health Guarantee Template - If the buyer can no longer keep the puppy, the breeder has the first right to reclaim it.
Florida Association of Realtors Forms - The walk-through inspection allows buyers to ensure property condition before closing.
Documents used along the form
The Hazard Bill of Lading form is essential for shipping hazardous materials, ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Alongside this form, several other documents are often utilized to facilitate the safe and legal transport of hazardous goods. Here’s a brief overview of some of these important documents:
- Shipper's Declaration of Dangerous Goods: This document provides detailed information about the hazardous materials being shipped, including their classification and handling requirements. It is crucial for ensuring that carriers and handlers are aware of the risks involved.
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS): The MSDS contains vital safety information about hazardous substances. It includes details on handling, storage, and emergency measures, helping ensure the safety of everyone involved in the shipping process.
- Emergency Response Guidebook (ERG): This guidebook offers first responders critical information on how to handle hazardous materials incidents. It provides instructions on containment, evacuation, and other emergency procedures, making it a key resource in case of an accident.
- Certificate of Compliance: This certificate verifies that the materials being shipped meet all relevant safety and regulatory standards. It assures all parties that the shipment is compliant with local, state, and federal regulations.
- Transport Document: This document serves as proof of the agreement between the shipper and the carrier. It outlines the terms of transport, including delivery instructions and liability terms, ensuring clarity and accountability throughout the shipping process.
Each of these documents plays a vital role in the safe and compliant transportation of hazardous materials. Together, they help protect not only the goods being shipped but also the people and environment surrounding the transportation process.
Misconceptions
Misconceptions about the Hazard Bill of Lading form can lead to confusion and potential legal issues. Here are seven common misconceptions and clarifications for each:
- The Hazard Bill of Lading is only for hazardous materials. Many believe this form is exclusively for hazardous materials, but it can also be used for non-hazardous goods. The key is to accurately describe the contents.
- Signing the form waives all liability. Some think that signing the Hazard Bill of Lading means the carrier cannot be held liable for any loss or damage. However, liability limitations are specified, and certain conditions still allow for claims.
- The form guarantees delivery of goods. There is a misconception that this form ensures delivery. While it outlines the responsibilities of the carrier, delivery is subject to various factors, including payment and the nature of the goods.
- All charges are included in the initial quote. Many assume that the initial freight quote covers all potential charges. In reality, additional fees may arise based on the nature of the shipment, such as storage or reconsignment costs.
- Claims must be filed immediately after loss or damage. Some individuals believe they must file claims right away. However, claims must be submitted in writing within nine months after delivery or after a reasonable time for delivery has passed.
- Only the shipper is responsible for the information provided. It is a common belief that only the shipper bears responsibility for the information on the form. In fact, both the shipper and the consignee share responsibility for ensuring accurate details.
- The form can be modified at any time. Some think they can make changes to the Hazard Bill of Lading after it has been signed. Modifications typically require mutual consent and should be documented properly to avoid disputes.
Understanding these misconceptions can help individuals navigate the complexities of shipping hazardous materials more effectively.
File Specs
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Origin | This form is printed in the United States by J. J. Keller & Associates, Inc. based in Neenah, WI. |
| Form Type | The document is a Hazardous Materials Straight Bill of Lading, categorized as original and non-negotiable. |
| Contact Information | For inquiries, the contact number is (800) 327-6868, available through the J. J. Keller website. |
| Hazardous Materials | The bill specifically indicates that it contains hazardous materials, necessitating special handling. |
| Liability Limitations | Liability for loss or damage may be limited under certain conditions, as per 49 U.S.C. regulations. |
| Claims Filing | Claims for loss or damage must be filed within nine months of delivery or after a reasonable delivery time has elapsed. |
| Freight Charges | The shipper is primarily responsible for freight and other lawful charges unless otherwise stated in writing. |
| Joint Liability | Shippers and agents are jointly liable for any loss or damage caused by hazardous goods if prior notice is not given. |
| Transport by Water | If transportation involves water, liability is governed by the carrier's bill of lading and applicable maritime laws. |
Key takeaways
When dealing with hazardous materials, filling out the Hazard Bill of Lading form accurately is crucial. Here are some key takeaways to keep in mind:
- Accurate Information is Essential: Ensure that all details, including the shipper, consignee, and the description of the hazardous materials, are filled out correctly. This prevents delays and potential legal issues.
- Understand Liability Limits: Be aware that the carrier's liability for loss or damage may be limited. Familiarize yourself with the terms regarding liability to protect your interests.
- Timely Claims Submission: If there is a loss or damage, claims must be filed in writing within nine months of delivery. Missing this deadline can result in losing the right to compensation.
- Proper Packaging and Labeling: The materials must be classified, described, and packaged according to regulations. This ensures safety during transportation and compliance with the law.
- Freight Charges Responsibility: The shipper is primarily responsible for all freight and lawful charges. Clearly indicate any payment instructions on the form to avoid misunderstandings.
By following these guidelines, you can navigate the complexities of shipping hazardous materials more effectively.